Income Tax Challan: How to Pay Your Income Tax Online?
- Rajesh Kumar Kar

- May 14, 2025
- 9 min read

One of the primary tasks that a taxpayer is expected to do is pay income tax, and the digital platform offered by the Income Tax Department of India makes this task reasonably easy. Very recently, an important facility regarding direct tax payments shifted from OLTAS 'e-payment: Pay Taxes Online' to the new 'e-Pay Tax' service, which taxpayers can avail on the e-Filing portal. Through this article, learn how to efficiently pay your taxes on the updated system.
Table of Contents
What is an Income Tax Challan?
An Income Tax Challan is the financial document used to pay income tax to the Government. It serves as a formal receipt of the tax payments made. Whether the payment is made towards personal income tax, corporate tax, or TDS, use of correct challan is very important. The Income Tax Department recognizes the Income Tax Challan as the proof of payment. Thus, it becomes an important element of the tax records.
Types of Income Tax Challan
There are different types of tax challans for different types of payments. Following are the types of Income Tax Challan:
Challan 280: This challan is used by the individual taxpayers for making the payment towards income tax, advance tax, and self-assessment tax.
Challan 281: It is used by businesses to deposit Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) and Tax Collected at Source (TCS).
Challan 282 and Challan 283: These challans are used for making payment towards other specific taxes.
Choosing the Correct Income Tax Challan
Choosing the right challan is important for ensuring that the tax payment is processed correctly. The type of challan is determined by the nature of tax to be paid. For instance, individuals paying advance tax would prefer Challan 280, whereas for making the TDS payment, business would require Challan 281. Using incorrect challan type may cause delay in the processing of challan and often creates confusion in tax records.
How to e-Pay Income Tax Online?
Because of digitization tax payments can be made online through the comfort of home or office, saving time and effort. Following are the steps for paying Income Tax Online:
Step 1: Access 'e-Pay Tax' Option
Go to 'Quick Links' on the homepage of the Income Tax Portal.
Click on 'e-Pay Tax', or in the search bar, type 'e-Pay Tax'.

Step 2: Fill in PAN/TAN and Mobile Number
Fill up PAN again for reconfirmation.
Enter the mobile number and click 'Continue'..

Fill in the 6-digit OTP received on the entered mobile number, and click 'Continue'.
Step 3: Select Assessment Year and Type of Payment
Choose the option '2024-25' from the drop-down list of 'Assessment Year.'
Under the head 'Type of Payment,' choose the 'Self-Assessment Tax (300)' option. Click 'Continue.'

Step 4: Fill Tax Payment Details
Correctly fill in the payment amounts in the given fields.
Check on the screen and match with pre−filled challan available on the portal.

Step 5: Select Mode of Payment
Choose the tax payment mode and bank to make the payment and click "Continue"
Tax payment would be possible or can be made through Internet banking, Debit Card, Credit Card, RTGS/NEFT, UPI you are free to visit the bank to make payment at the cash counter.

Step 6: Validate the Payment Information
Upon clicking on 'Continue,' details of the challan can be noticed.
Check validation of the payment details is done.
Click upon the "Confirm" payment option or click "Edit" if you want to edit it.

Step 7: Submit the Payment
Tick the checkbox provided to confirm acceptance of the Terms and Conditions.
Click on 'Submit To Bank'.

Step 8: Payment Confirmation
A message will be displayed that your tax payment has been successfully submitted.
Note: Once this is completed kindly download the challan as you will need the BSR number and challan number for the pay details to be entered while filing the return.
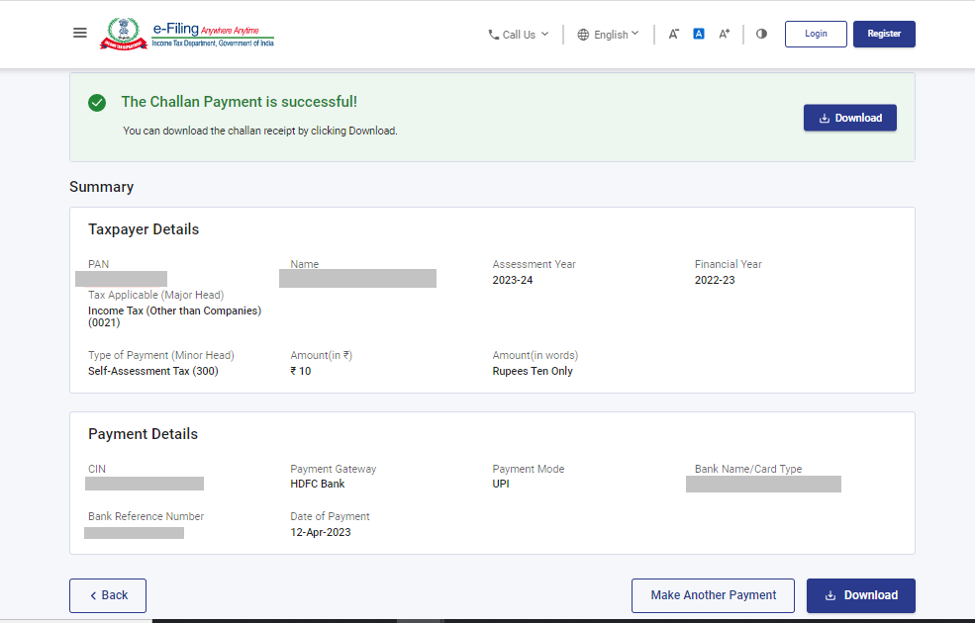
Step 9: Download the paid challan and share it with the Tax Expert of TaxBuddy to file your ITR.
How to Pay Income Tax Offline?
Following are the steps for making offline challan payments:
Locating the nearest bank branch: The first step is to locate the nearest bank branch authorized by the Income Tax Department for collecting the income tax. Most nationalized banks are equipped with such payment facilities. One can locate the nearest branch by checking the official website of the bank or through the Income Tax Department.
Filling out the complete challan form: Once the branch is located for challan payment, the next step is to fill out the challan form accurately. The details of PAN/TAN, the relevant assessment year, the type of payment, and the amount of tax. The input of accurate information will avoid errors and any issues with tax payments.
Advance Tax: Calculation and Payment
Advance Tax refers to the payment of estimated tax for the year in installments by the taxpayer, rather than in one lump sum at the end of the year. It is applicable when the total tax liability is in excess of INR 10,000 for the year. Payment advance tax ensures a consistent flow of revenue to the Government while also reducing the burden of large year-end tax payments on the taxpayer.
Calculation of Advance Tax Liability: The computation of advance tax liability involves the addition of total income for the financial year which includes salary, interest income, capital gains, and other sources. Apply the current rate of tax to determine the tax liability after considering TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) or eligible deductions under Section 80C, 80D, and likewise. The income tax rate is based on the slab rates applicable based on various income brackets.
Payment of Advance Tax: The Advance Tax can be paid using Challan 280 either online or offline. Online payment can be done through the Income Tax Department’s e-filing portal or in person at the authorized branches of the bank. The advance tax payments can be made in four installments throughout the financial year, that is, 15th June, 15th September, 15th December, and 15th March. To avoid interest charges on late payment, the deadlines for advance payment should be met.
Due Dates of Payment of Advance Tax for FY 2024-25

Non-payment of advance tax can result in penal interest levy under sections 234B and 234C.
Calculation of Tax Due on Total Income
To calculate the tax due on total income the total taxable income should be determined first accurately and then the applicable tax rates should be applied:
Estimating Total Taxable Income: The total taxable income is the estimate of the total annual income from all sources which includes salaries, profits and gains from business and profession, capital gains, income from rent, and other sources. The eligible deductions and exemptions are allowed to be deducted from the total income to determine the estimated taxable income.
Applying the Correct Tax Rates: After determining the taxable income, apply the tax rates based on the tax slabs of the financial year. The tax rates are different for different individual types since Income Tax classifies individuals based on income levels and age group. The correctness of tax due depends on the accuracy of applying the tax rates on the taxable income.
How to Avoid Common Mistakes with Income Tax Challan
When dealing with the Income Tax Challans, few common mistakes can result in unnecessary difficulty or even penalties. Following are the precautions to avoid common mistakes with Income Tax Challan:
Choosing the wrong type of challan: To avoid the misappropriation of tax payments, the selection of correct challan type is very important.
Providing incorrect details in challan: Important information such as PAN/TAN, assessment year, and the amount of tax to be paid should be entered in the challan correctly. Errors in these fields can lead to incorrect allocation of tax payments or processing delay.
Payment of late fees, interest, and penalties: The advance tax and the self-assessment tax should be paid within the deadlines to avoid late fees, interest and penalties.
Verification of Income Tax Challan Payment
The Income Tax Department (ITD) provides an easy way for taxpayers to verify the status of their challans. This verification helps confirm that the challan has been correctly processed. Taxpayers can also use the NSDL website to check the status of their payments. There are two main methods to verify a challan's status:
CIN-Based Verification: Taxpayers can track the status of a challan by providing details such as the Challan Identification Number (CIN), the date the challan was tendered, the BSR code of the bank branch where the payment was made, and the challan's serial number. They can also ensure that the correct tax amount was paid by entering the actual payment amount.
TAN-Based Verification: By using their Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number (TAN) and the challan tender date, taxpayers can retrieve the details of their Challan Identification Number (CIN). They can also verify the amount against a particular CIN to ensure that the correct amount was uploaded by the bank.
This system helps taxpayers stay informed and ensures the accuracy of their tax payments.
FAQ
Q1. Explain Income Tax Challan.
An Income Tax Challan is a form used for paying the income tax to the Government. It mentions about the payment type whether advance tax, self-assessment tax, regular assessment tax, and so on. It acts as a proof of payment of the income tax.
Q2. Is it possible to pay Income Tax Challan online?
Yes. The Income Tax Challan can be paid online via the Income Tax portal. This allows the assessee to pay various types of taxes like advance tax, self-assessment tax, and likewise online through the e-Payment facility.
Q3. Can an assessee correct the mistake made in the Income Tax Challan after payment?
The assessee can contact the bank where the payment is being processed within the stipulated time frame for making corrections in the Income Tax Challan. Corrections can be made to certain specific fields such as assessment year, PAN, and the type of tax payment.
Q4. What if the bank account is debited but the Income Tax Challan is not generated?
In cases where the bank account is debited and no tax challan is generated, the bank branch should be contacted where the payment was made. The bank will coordinate with the Income Tax Department to resolve the issue and then generate the challan.
Q5. How can an assessee verify whether the payment is made to the Income Tax Department or not?
Once the tax payment is made successfully, a Challan Identification Number (CIN) is generated, which is a proof of payment of the income tax challan. This CIN is useful in verifying the tax payment on the Income Tax Department’s website.
Q6. What are the details required to be filled in the Income Tax Challan?
Details such as PAN, assessment year, address, type of payment whether advance tax or self-assessment tax, and the bank through which the payment will be effected are required to be filled in the income tax challan.
Q7. Explain Challan 280.
Challan 280 is useful for the payment of income tax and corporate taxes. These taxes include advance tax, self-assessment tax, tax on regular assessment, tax on distributed profits and income, and additional charges.
Q8. There are different challans for different types of tax payments. Explain.
Yes. There are different types of challans for different types of tax payments. For instance, Challan 280 is for income tax, Challan 281 is for TDS/TCS, and Challan 283 is for other direct taxes.
Q9. How much time does it take to reflect the online tax payment in Form 26AS?
The tax payments made online are usually reflected within 3-7 working days in Form 26AS once the payment has been made.
Q10. Can an income tax payment be made using a credit card?
Yes. The e-payment facility allows taxpayers to make tax payments using net banking or debit/credit cards. However, this facility varies on the bank type and the terms and conditions.
Q11. What are the changes in the new e-Pay Tax service available on e-Filing portal as compared to the “OLTAS ePayment of Taxes” available on Protean Portal (previously NSDL)?
The new e-Pay Tax service facilitates the entire chain of activities related to the payment of direct taxes, from the generation of Challan (CRN) up to payment and recording of the payment history through the e-Filing portal of the Income Tax Department is made available to the Authorized Banks. The facility of filing Form 26QB/26QC/26QD/26QE is made available as part of this functionality.
Q12. Which are Authorized Banks for which tax payments are required to be made through the e-Filing portal?
At this point, all authorized banks have been enabled to make tax payments through the e-filing portal. The 28 authorized banks include Axis Bank, Bandhan Bank, Bank of Baroda, Bank of India, Bank of Maharashtra, Canara Bank, Central Bank of India, City Union Bank, DCB Bank, Federal Bank, HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, IDBI Bank, Indian Bank, Indian Overseas Bank, IndusInd Bank, Jammu & Kashmir Bank, Karur Vysya Bank, Kotak Mahindra Bank, Punjab & Sind Bank, Punjab National Bank, RBL Bank, South Indian Bank, State Bank of India, UCO Bank, and Union Bank of India. Taxpayers can make payments through Non-Authorised Banks with NEFT/RTGS and Payment Gateway (Bank of Maharashtra, Canara Bank, Federal Bank, State Bank of India, HDFC Bank & Kotak Bank offer this facility as of now) as the new modes of payment in e-Filing system.






Comments